In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive business environment, efficient and timely delivery of goods has become crucial for the success of enterprises in various industries. Whether it’s enterprise restaurant chains, diagnostics lab chains, e-commerce businesses, D2C businesses, retail, or grocery delivery businesses, the last mile of the logistics process plays a vital role in customer satisfaction and overall business performance. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have emerged as game-changers, revolutionizing the traditional last-mile logistics practices.
Traditionally, last-mile logistics has been a labor-intensive and costly process. Delivery personnel would manually plan the best routes, manage inventory, and handle customer queries and complaints. However, with the advent of AI and ML, logistics automation has become a reality, greatly streamlining and optimizing this crucial aspect of the supply chain.
AI-powered logistics automation offers a wide range of benefits, including improved delivery efficiency, better resource utilization, enhanced customer experience, and cost savings. By leveraging AI and ML algorithms, businesses can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns and trends, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their last-mile logistics operations.
Machine learning benefits
One of the key applications of AI and ML in last-mile logistics is route optimization. ML algorithms can analyze historical delivery data, consider factors such as traffic, weather conditions, and customer preferences, and suggest the most optimal routes for delivery personnel. This not only saves time and fuel but also reduces the chances of missed or delayed deliveries.
Additionally, machine learning enables predictive analytics, allowing businesses to anticipate customer demand and proactively manage inventory levels. By analyzing data from various sources such as past orders, customer demographics, and market trends, ML algorithms can forecast demand patterns and recommend optimal stocking levels. This prevents stockouts and overstock situations, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced inventory holding costs.
Another significant benefit of AI and ML in last-mile logistics is real-time tracking and visibility. With the help of AI-powered tracking systems and IoT devices, businesses can monitor the location and condition of their shipments in real-time. This enables proactive issue identification and resolution, ensuring that customers are updated about the status of their deliveries and minimizing the risk of lost or damaged packages.
AI in logistics
The integration of AI into logistics goes beyond route optimization and inventory management. It extends to various other aspects of the last-mile logistics process, including customer service, supply chain transparency, and delivery experience enhancement.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have become increasingly popular in the customer service domain. By leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms, businesses can provide 24/7 customer support, automate order tracking, and resolve customer queries and complaints in a timely manner. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also frees up human resources to focus on more complex tasks.
Furthermore, AI enables supply chain transparency by facilitating end-to-end visibility. By integrating AI-powered platforms with various stakeholders in the supply chain, businesses can track the movement of goods, monitor quality, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This not only helps in detecting and addressing bottlenecks but also enhances trust and accountability throughout the logistics ecosystem.
Lastly, AI and ML technologies are revolutionizing the delivery experience for customers. With the rise of autonomous vehicles and drones, businesses are exploring the feasibility of using AI-powered vehicles for last-mile deliveries. These vehicles can navigate autonomously, avoid obstacles, and optimize routes, ensuring safe and efficient delivery. Moreover, AI-powered delivery robots are being used in certain urban areas, providing contactless delivery services and reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional delivery methods.
In conclusion, the impact of artificial intelligence and machine learning on last-mile logistics cannot be overstated. From logistics automation and route optimization to improved inventory management and enhanced customer service, AI and ML have reshaped the way businesses approach the last stage of the supply chain. Enterprise restaurant chains, diagnostics lab chains, e-commerce businesses, D2C businesses, retail, and grocery delivery businesses can all benefit from embracing these transformative technologies. By leveraging the power of AI and ML, businesses can achieve greater operational efficiency, higher customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Now, let’s take a closer look at how Pidge, a leading logistics platform, utilizes AI and ML in its Last-Mile Logistics platform.
AI and ML Adoption at Pidge
Pidge is an innovative Last-Mile Logistics platform that leverages advanced AI and ML technologies to optimize delivery operations for businesses across various industries. By combining sophisticated algorithms with real-time data analysis, Pidge has successfully transformed the traditional last-mile logistics landscape.
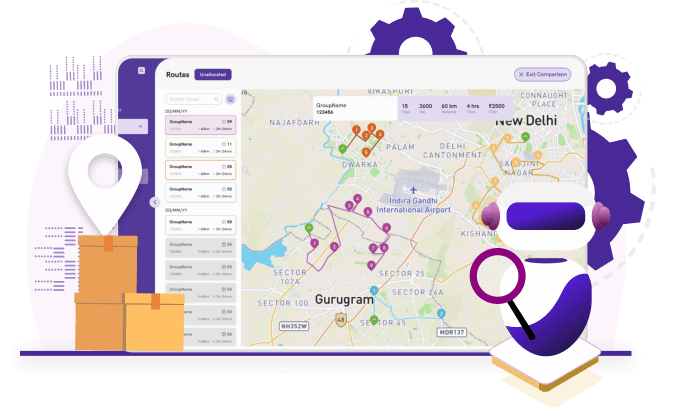

Here’s how Pidge’s AI & ML prowess is pushing the boundaries:
Hyper-Intelligence for Optimized Routes & Partner Selection: Forget static routes and guesswork. Pidge’s AI engine acts as a dynamic logistics mastermind, constantly analyzing real-time traffic patterns, weather conditions, partner capabilities, and historical data. This empowers it to choose the fastest, most cost-effective route for every single order, leading to:
Reduced delivery times: Get your packages to customers quicker, exceeding expectations and boosting satisfaction.
Optimized costs: Eliminate unnecessary expenses by leveraging the most efficient partner for each delivery.
Enhanced flexibility: Adapt to unexpected surges or disruptions with real-time route adjustments, ensuring seamless operations.
Automated Workflows & Streamlined Operations: Ditch the manual processes that bog down your team. Pidge’s ML automates repetitive tasks like:
Repeat Orders: Eliminate manual repeat order creating, routing, and partner allocation, saving time and reducing errors.
Routing: Create ML-powered custom routes to fit your delivery needs and improve operational productivity.
This automation not only boosts efficiency and accuracy but also frees up your team to focus on higher-level strategic initiatives that drive business growth.
Data-Driven Decisions & Continuous Improvement: Pidge goes beyond just delivering packages; it generates valuable data insights. We leverage ML models to analyze every aspect of your deliveries, uncovering hidden patterns and trends. This actionable intelligence empowers you to:
Identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows: Pinpoint areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to continuously refine your last-mile strategy.
Predict customer behavior and preferences: Gain deeper insights into your customer base, enabling personalized delivery experiences and targeted marketing campaigns.
Measure and track KPIs: Monitor key performance indicators to ensure you’re meeting your goals and identify areas for further optimization.
The impact is undeniable: Faster deliveries, lower costs, happier customers, and a data-driven, future-proof last-mile operation. Pidge isn’t just delivering your packages, it’s unlocking the true potential of your business.
Ready to join the last-mile revolution? Contact Pidge today and discover how AI and ML can transform your deliveries.

Leave a Reply