In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, last-mile delivery has become a crucial aspect of supply chain and logistics operations. The last mile, which refers to the final leg of the delivery process from the distribution center to the end customer’s doorstep, is often considered the most challenging and expensive part of the entire supply chain. As a result, companies are continuously exploring innovative delivery solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. This article will discuss some of the emerging trends in last-mile delivery solutions that are revolutionizing the industry.
Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics are transforming the way goods are delivered to customers. This technology enables companies to streamline their last-mile delivery processes by using drones, autonomous vehicles, and robotic delivery agents. Drones, for example, can navigate through urban areas and deliver packages within a short period, bypassing traffic congestion. Autonomous vehicles can operate on predetermined routes, eliminating the need for human intervention and reducing delivery time. Robotic delivery agents can carry out last-mile deliveries in crowded places, providing convenience and efficiency.
AI-powered Routing and Optimization: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a significant role in optimizing last-mile delivery routes. By using historical data, real-time traffic information, and machine learning algorithms, AI-powered routing systems can suggest the most efficient routes for delivery drivers. These systems take into account various factors such as traffic congestion, weather conditions, and customer preferences to ensure timely and cost-effective deliveries. The use of AI can help companies save fuel costs, reduce emissions, and enhance overall delivery performance.
Crowdshipping and Peer-to-Peer Delivery: Crowdshipping and peer-to-peer delivery platforms are disrupting the traditional last-mile delivery model. These platforms connect individuals who are willing to deliver packages with shippers who need their goods transported. Crowdshipping enables companies to leverage underutilized resources, such as extra space in private vehicles, to fulfill last-mile deliveries. By tapping into a vast network of individuals, crowd-shipping platforms can offer more flexible and cost-effective delivery options. Peer-to-peer delivery also fosters a sense of community and trust among the participants.
Smart Lockers and Pickup Points: Smart lockers and pickup points are gaining popularity as convenient alternatives to doorstep delivery. These solutions allow customers to collect their packages from secure lockers or designated pickup locations at their convenience. Smart lockers are equipped with advanced security features such as secure access codes or biometric authentication, ensuring the safety of packages. Pickup points, strategically located in residential areas or commercial centers, enable customers to pick up their orders during extended hours. By offering multiple pickup options, companies can reduce delivery failures and enhance customer satisfaction.
Sustainable and Green Delivery: With growing environmental concerns, sustainable and green last-mile delivery solutions are gaining momentum. Companies are increasingly adopting electric vehicles, bicycles, and even electric drones for deliveries. These eco-friendly options contribute to reducing carbon emissions and minimizing the environmental impact of logistics operations. In addition to using green vehicles, companies are also exploring innovative packaging materials, such as biodegradable or recyclable materials, to minimize waste. Sustainable delivery practices not only resonate with environmentally conscious customers but also help companies comply with regulatory requirements and build a positive brand image.
Challenges in Last-Mile Delivery
While there are numerous innovative solutions in the last-mile delivery space, it is essential to address the challenges that companies face in implementing these solutions effectively. Understanding these challenges can help supply chain and logistics operations managers find appropriate strategies to overcome them.
Traffic Congestion: One of the most significant challenges in last-mile delivery is navigating through traffic congestion in urban areas. Traffic congestion not only slows down delivery times but also increases fuel consumption and operational costs. To tackle this challenge, companies can leverage AI-powered routing systems to find the most efficient routes, consider alternative delivery modes such as drones or bicycles, and collaborate with local authorities to optimize traffic management during peak hours.
Delivery Density: Delivery density refers to the concentration of delivery points within a specific geographic area. Low delivery density in rural or sparsely populated areas makes it economically challenging to offer cost-effective last-mile delivery services. In such cases, companies can explore innovative partnerships with local businesses to consolidate deliveries or utilize crowd-shipping platforms to tap into the existing transportation network in the area.
Customer Expectations: Customers have increasingly high expectations when it comes to last-mile delivery. They expect fast, reliable, and convenient delivery options, along with real-time tracking and notifications. Meeting these expectations requires companies to invest in advanced tracking technologies, efficient communication systems, and customer-centric service policies. Providing flexibility in delivery time slots, offering weekend or after-hours deliveries, and enabling customers to choose their preferred delivery options can significantly enhance customer satisfaction.
Future of Last Mile Delivery
The future of last-mile delivery looks promising with the continuous development of technology and innovative solutions. As customer demands evolve and companies strive to stay ahead of the competition, several trends are expected to shape the future of last-mile delivery.
Delivery by Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles, including self-driving cars and delivery robots, are expected to play a more significant role in last-mile delivery. These vehicles can operate without human intervention, reducing labor costs, and enabling efficient deliveries. However, challenges such as regulatory frameworks, safety concerns, and public acceptance need to be addressed before the widespread adoption of autonomous delivery vehicles.
Hyperlocal Delivery Networks: Hyperlocal delivery networks are expected to gain traction in the future. These networks focus on optimizing last-mile deliveries within a specific neighborhood or city, allowing for faster and more efficient delivery times. By establishing small warehousing facilities close to the end customers and utilizing local delivery partners or micro-fulfillment centers, companies can enhance their delivery capabilities and provide same-day or even on-demand deliveries.
Integration of IoT and Blockchain: The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize last-mile delivery. IoT devices can provide real-time data on package location, temperature, and condition, ensuring transparency and security throughout the delivery process. Blockchain technology can enhance traceability, enable smart contracts, and improve trust among all stakeholders involved in the supply chain. This integration can streamline operations, reduce fraud, and improve accountability in last-mile delivery.
Pidge: Leading the Last-Mile Revolution with AI and Innovation
While innovative trends paint a promising future for last-mile delivery, navigating the evolving landscape requires partners who understand the challenges and translate technology into tangible solutions. That’s where Pidge steps in, poised to revolutionize the way last-mile logistics happen.
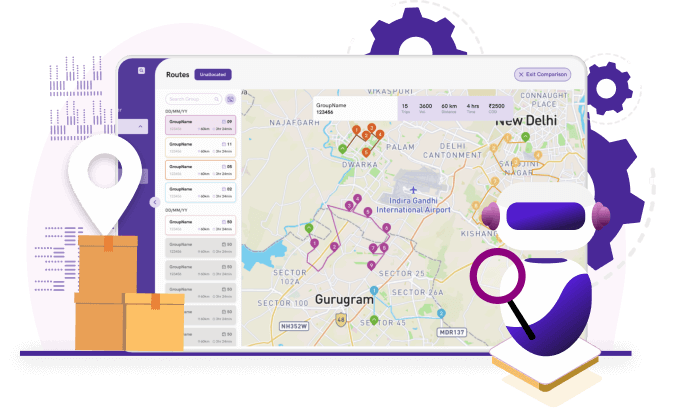

Powered by our cutting-edge AI engine, MORRE™ (Multiple Optimization Route Recommendation Engine), Pidge tackles last-mile hurdles head-on:
Conquering Traffic Congestion: MORRE™ dynamically adjusts routes in real-time, weaving through urban snarls with AI-powered rerouting. Say goodbye to delays and fuel-guzzling detours.
Optimizing Delivery Density: Our flexible approach adapts to diverse landscapes. In sparse areas, Pidge leverages crowdsourced delivery networks and strategic partnerships to ensure efficient and cost-effective service.
Surpassing Customer Expectations: We empower you to exceed even the highest expectations. Pidge offers a spectrum of features, from flexible delivery slots and real-time tracking to weekend and after-hours options, ensuring convenience and delighting your customers.
But Pidge goes beyond just smart routing:
Advanced Analytics: Gain invaluable insights into your delivery operations with granular data and actionable reports. Identify optimization opportunities, predict customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions for a continuously improving last-mile strategy.
Seamless Integration: Pidge seamlessly integrates with your existing systems, eliminating data silos and streamlining your workflow. Our platform is designed for user-friendliness, empowering your team to adapt and thrive in the face of change.
Sustainable Focus: We understand the importance of eco-friendly practices. Pidge promotes sustainable deliveries through route optimization, electric vehicle partnerships, and innovative packaging solutions, minimizing your environmental footprint and building a responsible brand image.
Pidge is more than just a platform; it’s a trusted partner in your last-mile success. We help you navigate the changing landscape, optimize your operations, and exceed customer expectations.
Ready to join the last-mile revolution? Embrace the power of AI and innovation with Pidge. Contact us today and unlock the true potential of your last-mile delivery operations.

Leave a Reply